-
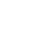
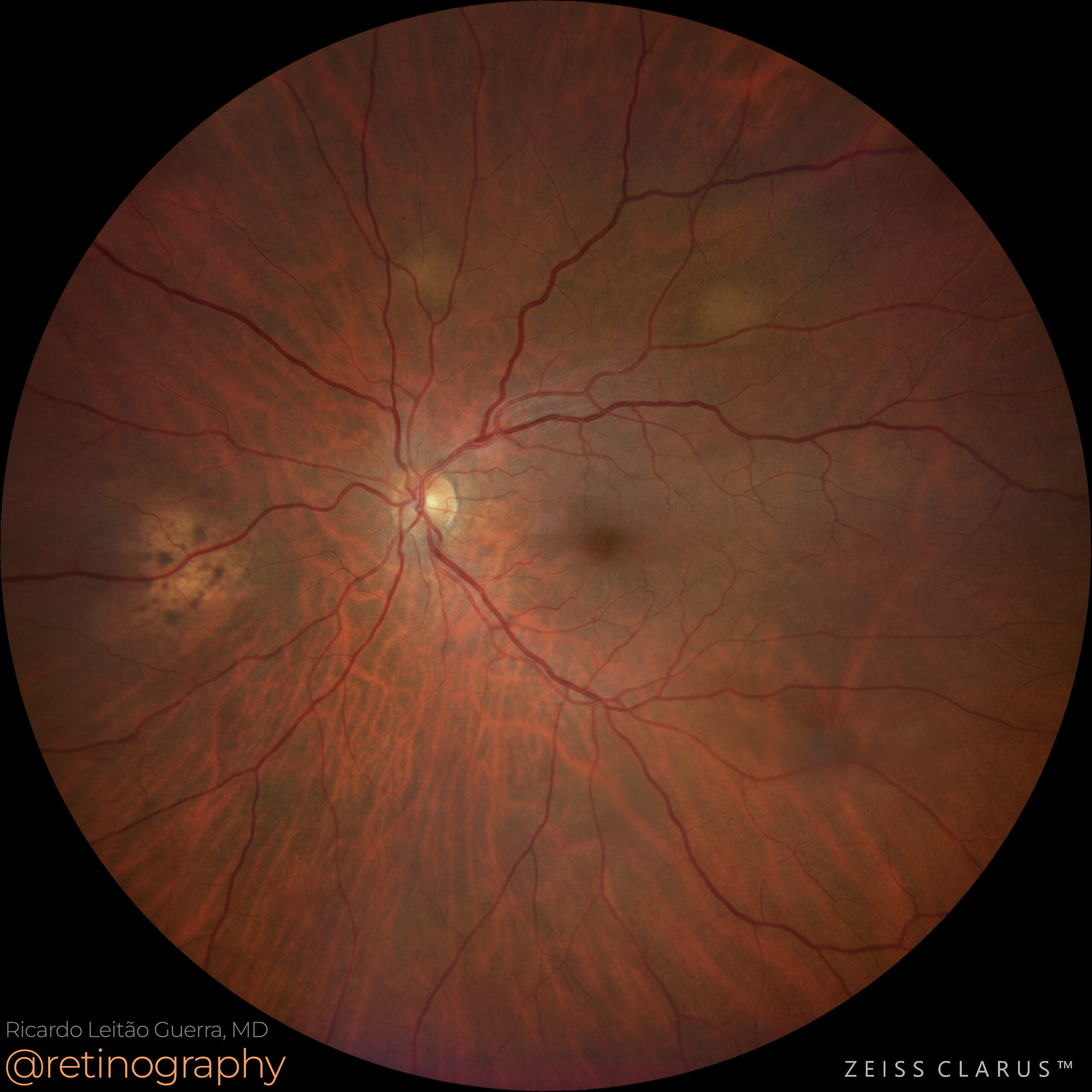
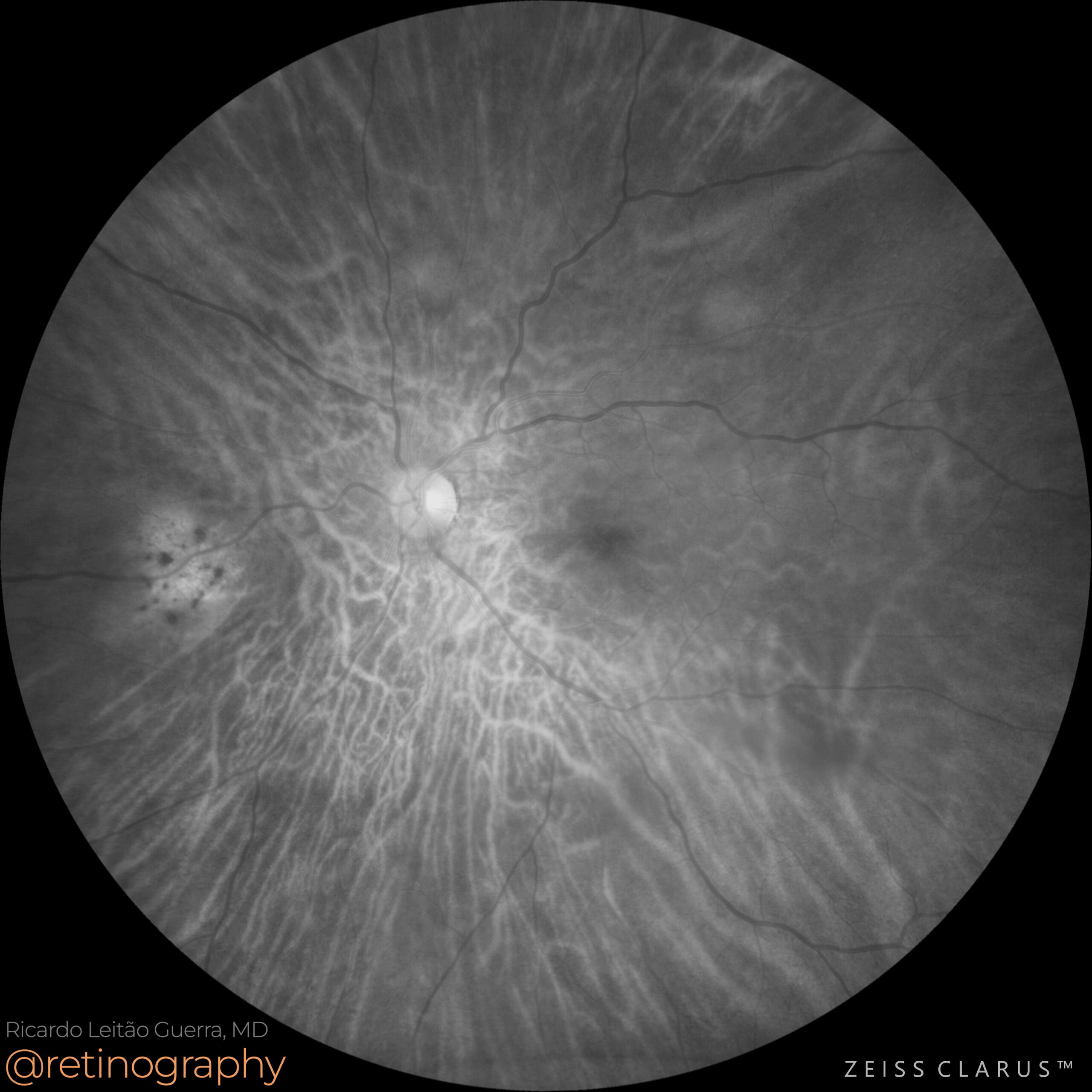
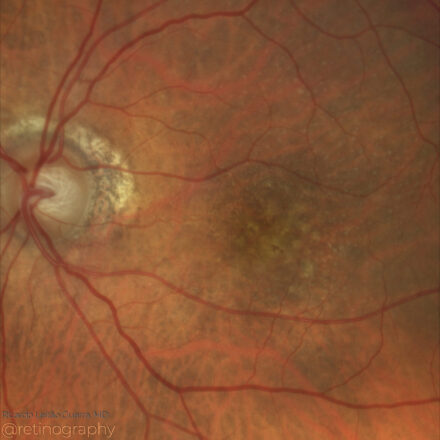
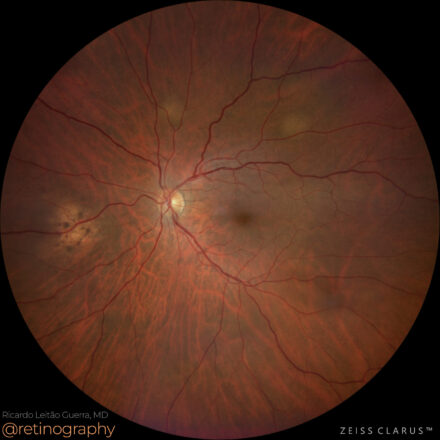
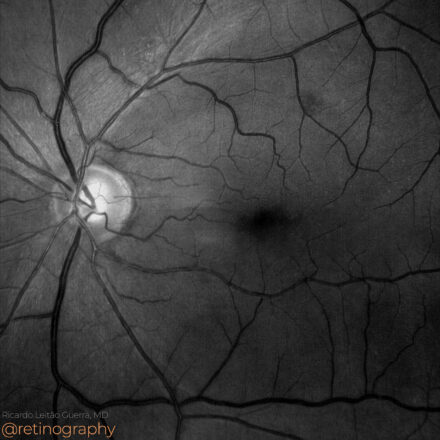
Choroidal Metastases
 74yo
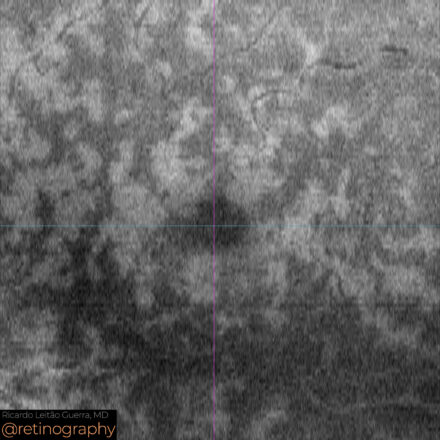
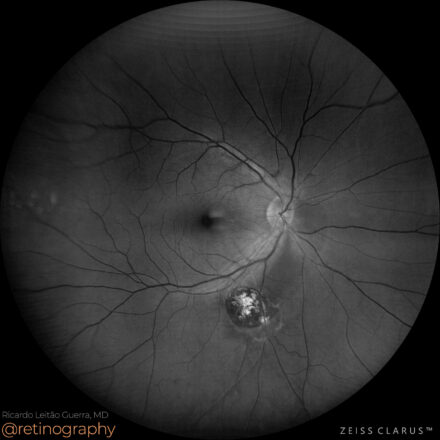
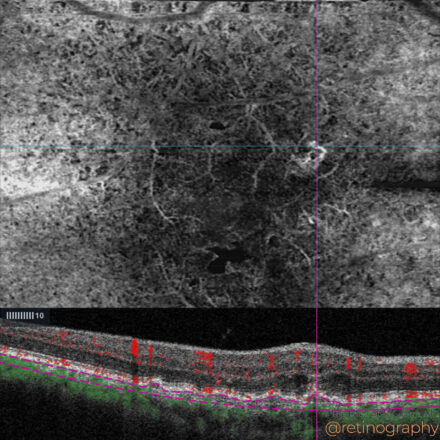
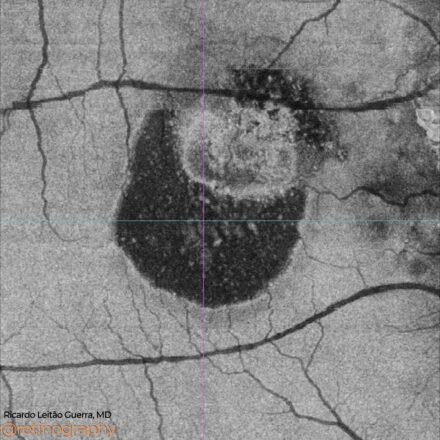
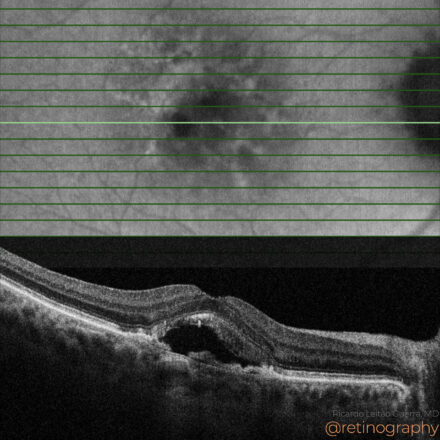
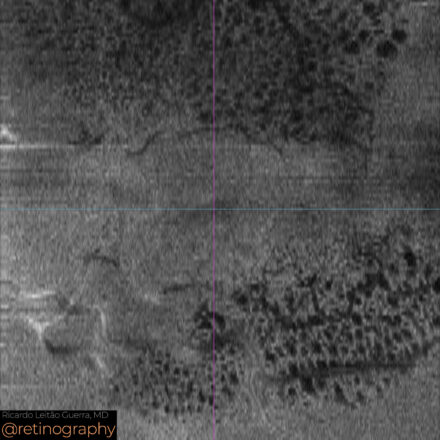
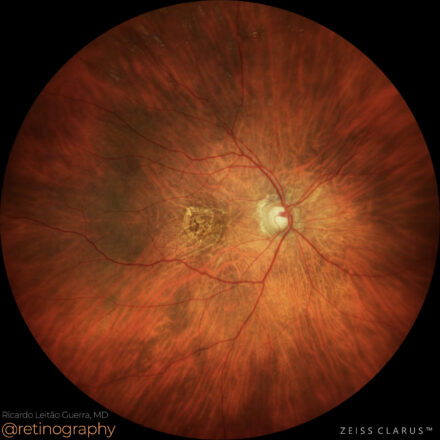
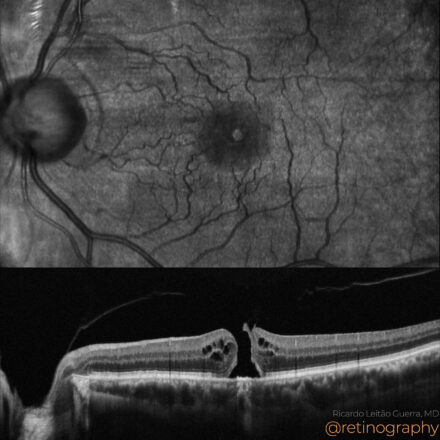
74yo Choroidal metastasis is the most common ocular malignancy, often originating from breast or lung cancer. It typically presents as a yellowish, dome-shaped mass in the posterior pole of the eye. Diagnosis is mainly achieved through clinical examination, imaging techniques like ultrasound or OCT, and sometimes biopsy. Treatment varies but may include systemic therapy, radiotherapy, or local interventions to manage vision-threatening complications.
#ChoroidalMetastasis #OcularOncology #retina #oftalmo #ophthalmology #oftalmologia #oftalmología #ophtalmologie #офтальмологія #офтальмология #οφθαλμολογία #retinography2024 #CIRRUS6000 #CLARUS700 #ZEISSRETINAWORKFLOW
Other Cases
-
PAMM due to Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
 63yo
63yo Paracentral Acute Middle Maculopathy (PAMM) secondary to Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) is characterized by ischemia in the intermediate and deep capillary plexus. En-face OCT reveals a distinctive “fern-like” pattern, representing hyperreflective bands in the middle retinal layers. This pattern highlights the areas of ischemia, allowing for detailed visualization of […]
-
Ocular toxoplasmosis
 53
53 Ocular toxoplasmosis can cause retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) defects due to inflammation and scarring. Blue light reflectance imaging is particularly helpful in identifying these RNFL changes, as it enhances the visualization of subtle defects and disruptions in the nerve fiber layer. This imaging modality aids in detecting structural damage […]
-
AMD: Type 3 MNV
 74
74 In Type 3 macular neovascularization (MNV), OCT-Angiography B-scan with decorrelation signal is essential for detecting intraretinal neovascularization. The decorrelation signal appears as flow signals within the retinal layers on OCT-A, indicating abnormal blood vessels and helping to confirm the presence of Type 3 MNV. This non-invasive imaging technique is critical […]
-
Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
 74
74 In polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV), en-face OCT imaging at the level of the ellipsoid zone (EZ) is valuable for highlighting subretinal fluid. This imaging technique provides a detailed view of fluid accumulation beneath the retina, allowing for precise assessment of the extent and distribution of the fluid associated with PCV. […]
-
AMD: RPE tear
 78yo
78yo In age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) tear is a serious complication often associated with pigment epithelial detachments. Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) shows hypoautofluorescence in the area of the tear due to the loss of RPE, while hyperautofluorescence may outline the borders. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) provides cross-sectional […]
-
Degenerative cystoid spaces following ERM peeling
 74yo
74yo Degenerative cystoid spaces can develop after epiretinal membrane (ERM) peeling, and they are best visualized using en-face OCT. This imaging technique provides detailed top-down views of the retina, revealing the cystoid spaces within the retinal layers. These spaces represent areas of retinal degeneration and fluid accumulation, which can affect visual […]
-
Neovascular AMD
 90
90 In neovascular age-related macular degeneration (AMD), multimodal evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis and management. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) detects subretinal and intraretinal fluid, indicating neovascular activity. Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) helps assess retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) status. Combining these modalities provides a comprehensive view of the disease for optimal treatment […]
-
Commotio Retinae
 14yo
14yo Commotio retinae is a traumatic retinal injury characterized by glistening gray-white opacification of the retina, commonly affecting the outer retinal layers. Color channel analysis can help highlight subtle changes in different retinal layers. The opacification resolves within weeks, but in some cases, permanent damage such as macular hole or retinal […]
-
Macular hole
 72yo
72yo In macular holes, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) can reveal the presence of vitreous traction adhered to the edges of the hole. This traction can contribute to the formation or persistence of the hole by exerting stress on the surrounding retinal tissue. OCT provides detailed cross-sectional imaging, showing the extent of […]
-
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
 90
90 In age-related macular degeneration (AMD), drusen and drusenoid pigment epithelial detachment (PED) are common findings. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) reveals drusen as hyperreflective elevations between the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and Bruch’s membrane, while drusenoid PED appears as larger sub-RPE accumulations. Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) highlights areas of RPE stress with […]
-
Choroidal Metastases
 74yo
74yo Choroidal metastasis is the most common ocular malignancy, often originating from breast or lung cancer. It typically presents as a yellowish, dome-shaped mass in the posterior pole of the eye. Diagnosis is mainly achieved through clinical examination, imaging techniques like ultrasound or OCT, and sometimes biopsy. Treatment varies but may […]
-
Arcuate RNFL defect
 60yo
60yo An inadvertent touch to the retina during ILM peeling can cause an arcuate defect, best visualized using blue light reflectance. This imaging modality enhances the contrast, making subtle retinal damage more apparent. Early detection of such defects is crucial for monitoring post-surgical recovery and ensuring no further retinal complications arise. […]