-
DONFL
 78yo
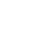
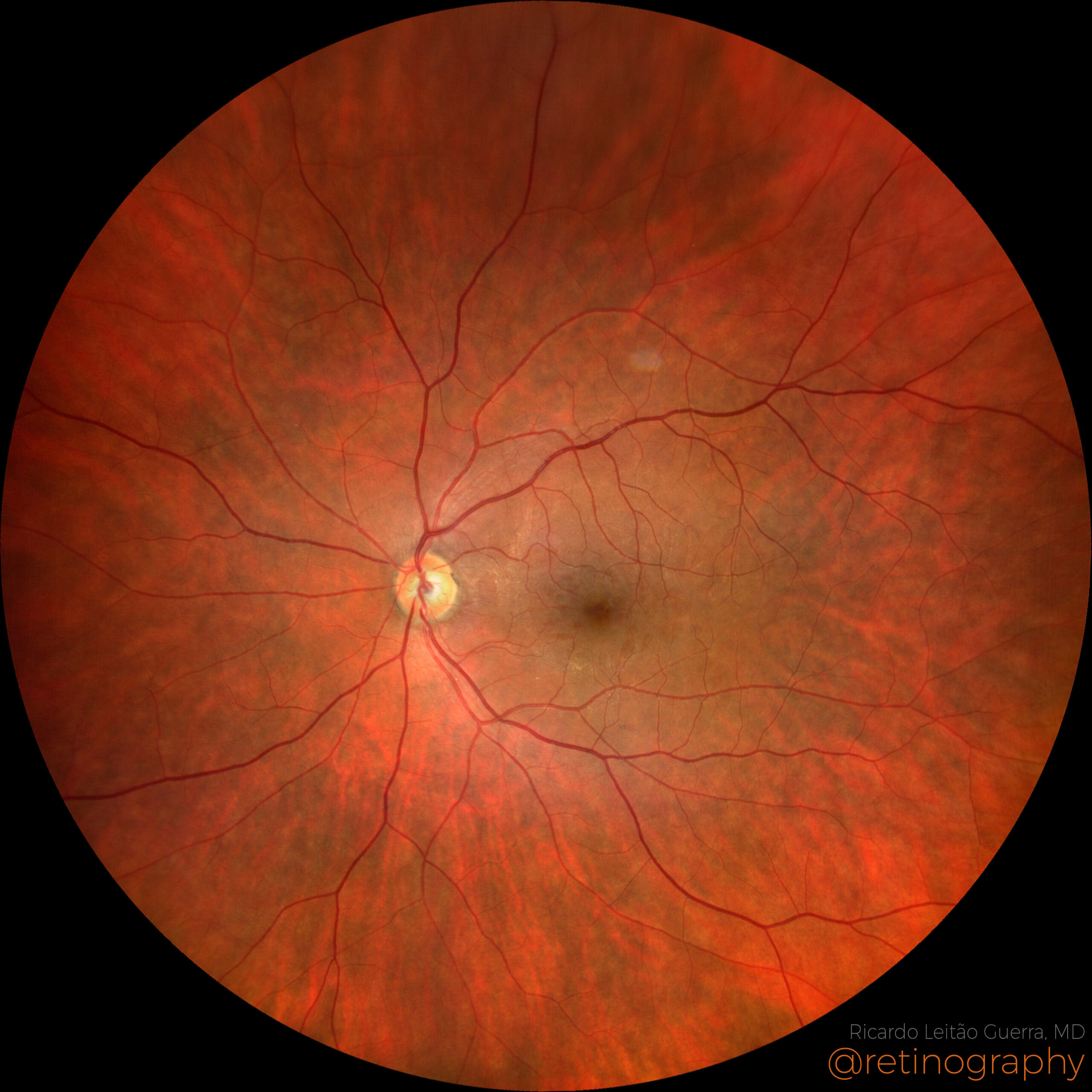
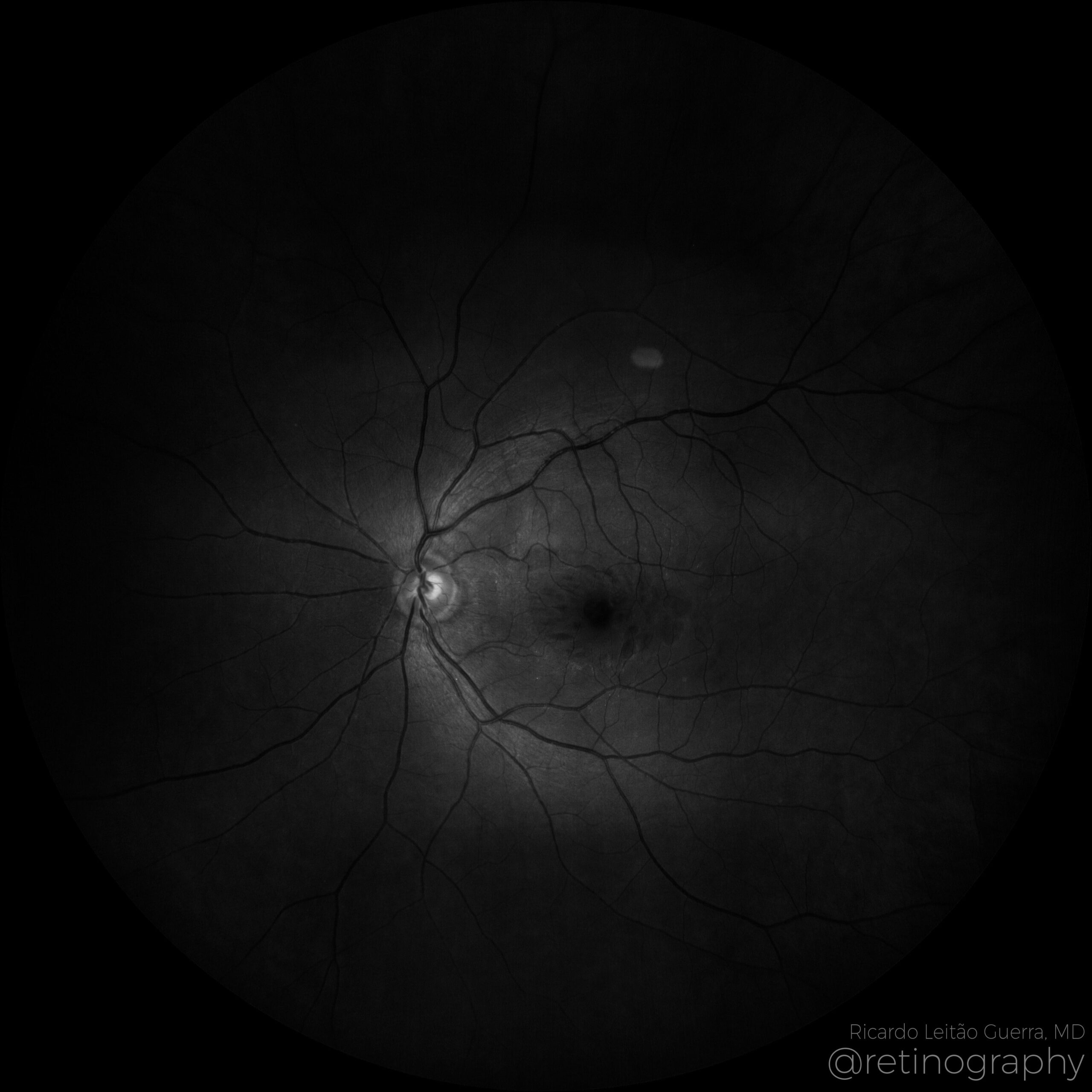
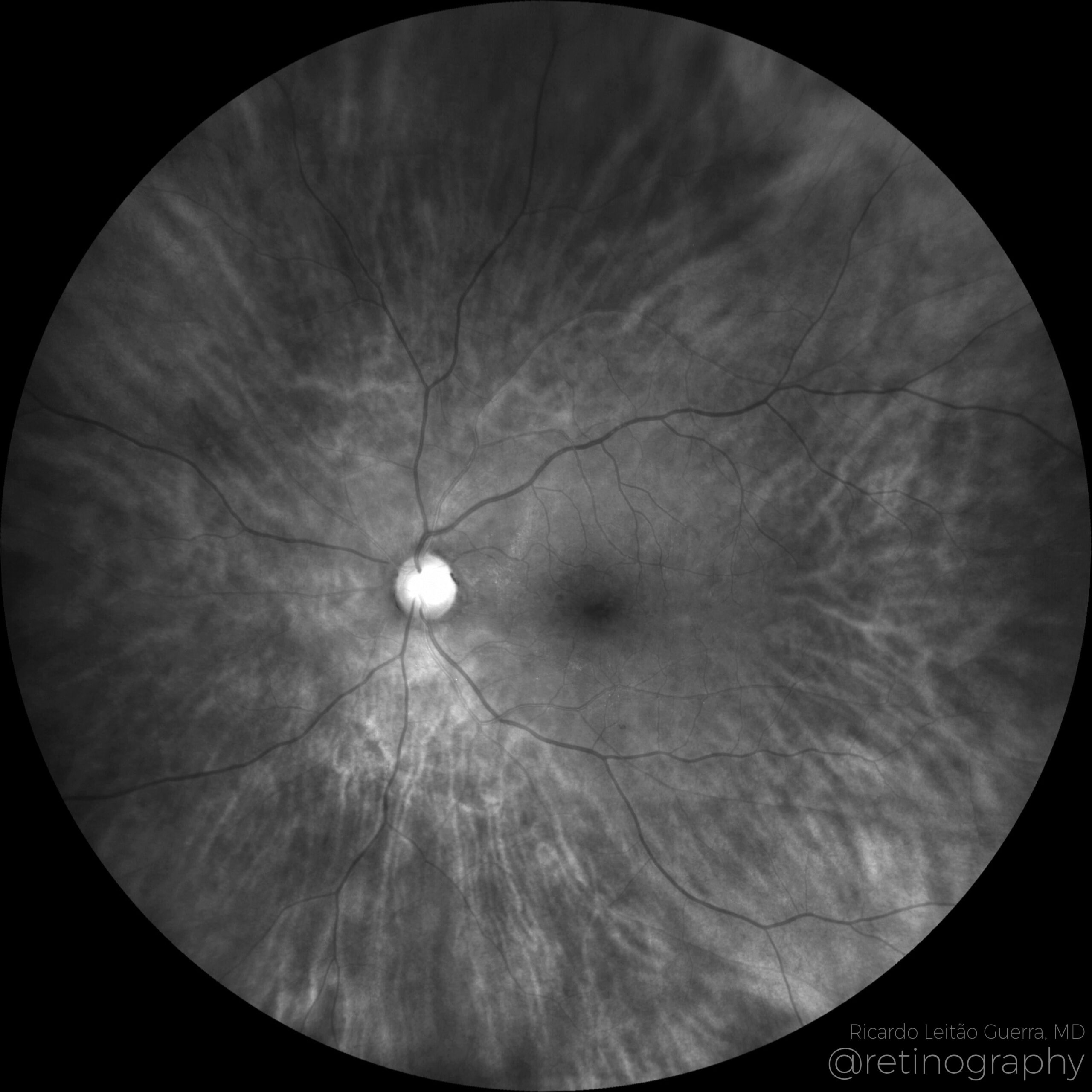
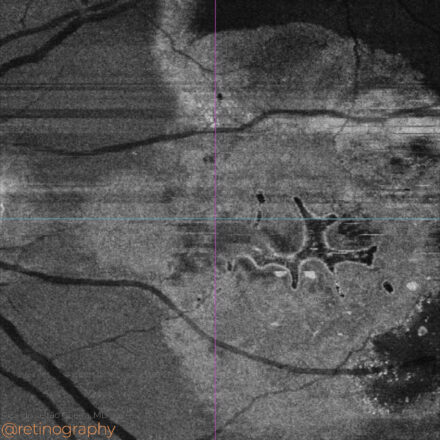
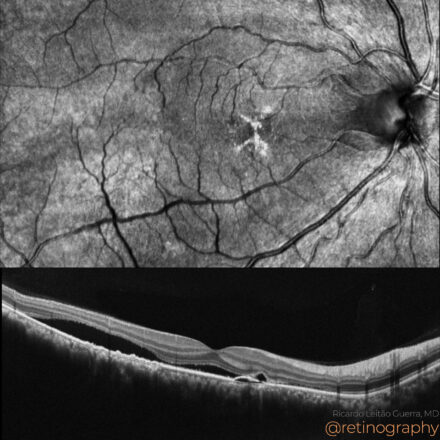
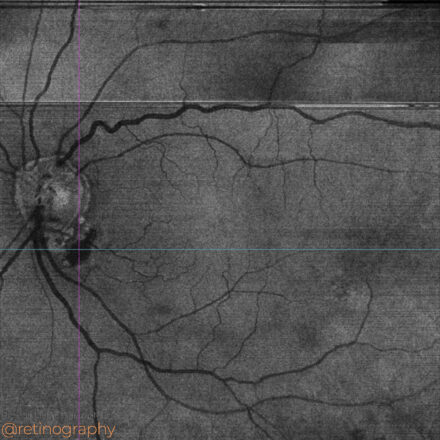
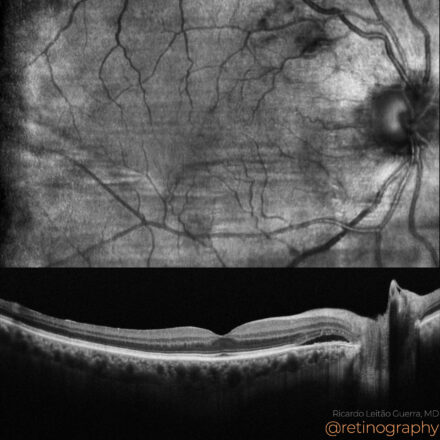
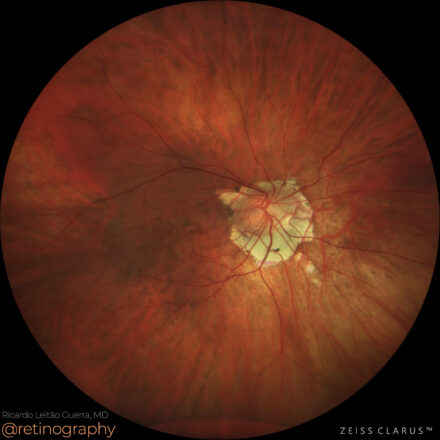
78yo Multimodal imaging analysis in a a case of Dissociated Optic Nerve Fiber Layer (DONFL) appearance after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular hole. The DONFL appears after vitrectomy, showing as slit-like, arcuate defects in the retinal nerve fiber layer, particularly visible using Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). The analysis through different color channels enhances visualization, aiding in distinguishing these alterations from other retinal pathologies. Understanding the impact of color channel adjustments is critical for accurate assessment and documentation of DONFL in post-surgical patients.
Disclosure: All images featured in this post were acquired and analyzed using devices integrated within the Zeiss Retina Workflow. This ensures high-quality, detailed visual data for comprehensive assessment.
Other Cases
-
AMD: Outer retinal tubulations
 77yo
77yo In age-related macular degeneration (AMD), outer retinal tubulations (ORT) can present unique patterns on en-face OCT, often resembling intraretinal fluid (IRF), leading to potential misdiagnosis. In the presented case, en-face imaging shows ORT as hyporreflective interconnected branching networks extensions surrounded by a hyperreflective borders, while dark areas without hyperreflective borders […]
-
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
 40yo
40yo In Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSC), serous retinal detachment and serous pigment epithelial detachment (PED) are hallmark findings. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) reveals a hyporeflective space beneath the neurosensory retina and PEDs, often associated with focal RPE abnormalities. The leakage site at the RPE can be identified on OCT as a […]
-
Situs inversus: Degenerative myopia
 40yo
40yo In degenerative myopia, situs inversus refers to the tilted insertion of the optic disc, commonly associated with retinal and choroidal changes. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) B-scan often shows tilted scans due to the oblique orientation of posterior pole structures. This tilting can distort retinal layer visualization, requiring careful interpretation to […]
-
Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy
 79yo
79yo Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV) should be investigated when subretinal fluid (SRF) is observed adjacent to the optic disc. En-face OCT imaging at the level of the ellipsoid zone (EZ) is a valuable tool for detecting SRF in these cases, providing a detailed view of fluid distribution and its impact on […]
-
AMD: Disciform scar
 77yo
77yo In advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a disciform scar represents the end stage of neovascular AMD. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) shows hyperreflective fibrotic tissue replacing normal retinal layers, with possible subretinal fluid or retinal thinning. Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) reveals hypoautofluorescence due to retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) atrophy, with surrounding hyperautofluorescence […]
-
Central Serous Chorioretinopathy
 48yo
48yo In acute Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSC), Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) reveals subretinal fluid as a hyporeflective space between the neurosensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). The absence of significant intraretinal fluid differentiates CSC from other causes of macular edema. OCT is essential for diagnosing, monitoring resolution, and assessing […]
-
Multifocal Best’s vitelliform dystrophy
 33yo
33yo Multifocal Best vitelliform dystrophy is a rare retinal condition characterized by multiple yellowish vitelliform lesions scattered across the posterior pole. Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) shows hyperautofluorescent lesions due to lipofuscin accumulation in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Over time, areas of hypoautofluorescence may appear, indicating RPE atrophy. FAF is crucial for […]
-
Drusen
 37yo
37yo The presence of drusen in a young woman may suggest inherited or systemic conditions rather than typical age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Conditions like familial drusen, basal laminar drusen, or early-onset drusen should be considered. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) can reveal their size and location, and fundus autofluorescence (FAF) may show […]
-
Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
 81yo
81yo Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV) should be investigated when subretinal fluid is observed adjacent to the optic disc. Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) is useful in these cases, as it highlights retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) changes. Areas of hyperautofluorescence indicate RPE stress, while hypoautofluorescence suggests atrophy, aiding in the identification of PCV-related abnormalities. […]
-
Secondary macular telangiectasia (BRVO)
 70yo
70yo Secondary macular telangiectasia due to branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) is characterized by vascular changes in the macula. Fluorescein angiography (FA) reveals dilated and tortuous macular capillaries, areas of leakage, and capillary telangiectasia. FA helps assess the extent of macular involvement, guiding management decisions such as anti-VEGF therapy to address […]
-
Myopic macular neovascularization
 40yo
40yo Myopic macular neovascularization (MNV) located in the superior parafoveal region can be effectively treated with anti-VEGF therapy. After treatment, the lesion appears as an area of hypoautofluorescence on fundus autofluorescence (FAF), indicating resolution of neovascular activity and associated damage to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). FAF is a useful tool […]
-
Ocular toxoplasmosis: Chorioretinitis scars
 67yo
67yo In ocular toxoplasmosis, chorioretinitis scars can reveal underlying structures such as the posterior long ciliary artery and nerve. These become visible due to the localized atrophy of the retina, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and choroid, allowing clearer visualization of the deeper scleral and vascular structures. #Toxoplasmosis #ChorioretinitisScar #PosteriorCiliaryArtery #RetinaImaging #FAF […]